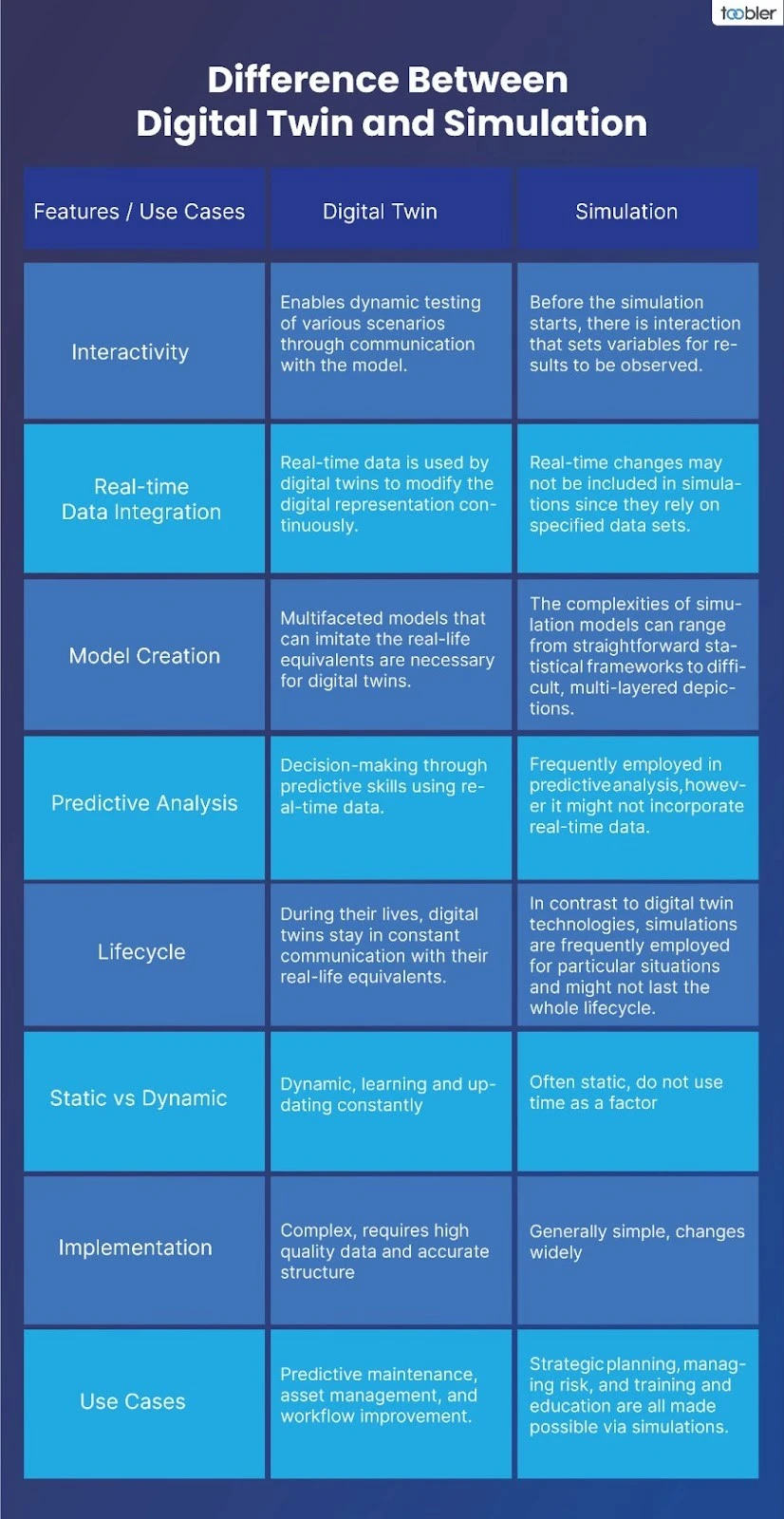
-Real-Time Data Integration
Digital twins generate a dynamic, digital representation of tangible objects, enabling real-time operation, evaluation, analysis, and improvement. This constant stream of data from sensors and other IoT devices allows current assessment, analysis, and improvement.
Think about the use of digital twins in manufacturing, where they are used in smart factories with sensor-equipped machinery. A production line's digital twin can get real-time information on machine performance, identify irregularities, and anticipate the need for repairs before any malfunctions happen. By being proactive, downtime is reduced, and total productivity is raised.
In contrast, simulations use pre-established circumstances and data. They are perfect for planning and hypothesis testing because they simulate how systems behave under particular circumstances using data from theory or the past.
Financial institutions, for example, frequently utilize simulations to test investment approaches and mimic market behaviors. They can predict the success of various portfolios under numerous monetary situations. This helps with risk estimation and decision-making. They do this by using past market data and projected future patterns.
Please Read: How digital twin projects are transforming the Manufacturing industry. Here
1. Static Simulation vs Active Digital Twin
Precise design features and parameters are essential for simulations. Once the digital model has been generated, the parameters cannot be altered unless the designer enters new ones. Only details on that particular design are available from the static model. Engineers must create a new simulation from the start for new designs.
For example, engineers test new aircraft designs via simulators. By entering parameters such as wind speed, altitude, and load, they can forecast the aircraft's performance in various scenarios. Before the aircraft ever takes to the air, these simulations are essential for improving the design and guaranteeing safety.
Conversely, digital twin technology begins in the same manner as a simulation. Nevertheless, because it uses real-time data, the simulation will continually alter.
Digital twins will always search for active simulation methods to improve the product. For instance, active simulation can mimic the product's lifetime. This helps give designers access to data that is beyond the scope of a straightforward simulation.
Consider digital twins in smart cities. Urban planners use digital twins to maintain metropolitan infrastructure. For example, a digital twin of a city's water distribution system continuously receives data regarding water flow, pressure, and quality. This real-time data facilitates effective water distribution, leak detection, and supply management.
Also Read: Digital Twin Use Cases. Here
2. Precision and Accuracy
Digital twins are known for having extremely high levels of precision and accuracy. They ensure that the digital model is an accurate, current imitation of its physical equivalent by constantly gathering data in real-time from physical assets. Businesses can make well-informed judgments based on actual situations because of this accuracy.
Take the example of digital twins in medicine. A hospital may utilize a patient's cardiac digital twin. Due to this twin, physicians may access an exact picture of the heart's current condition. This picture changes instantaneously with data from many medical equipment and sensors. This precision is essential for organizing surgeries or other medical procedures to ensure the best potential patient outcomes.
Even though they are helpful, simulations use pre-established data collections and presumptions to model results. They may not consider all variables or changes that occur in real-time because their results are estimates based on the input data.
For instance, city planners use traffic simulations to develop road networks and control traffic. These simulations use historical traffic data and anticipated growth rates to predict future traffic patterns. Although the results are approximations and may require revisions as actual conditions vary, they are helpful in planning construction efforts.
3. Possible vs. Actual
While a digital twin mimics what happens to a given product in the real world, a simulation only represents what might occur to an object. The designer's creativity is the only limit to what can be altered in a simulation.
However, because a digital twin provides accurate input, the designer may assess whether it is functioning as planned and then decide what needs to be improved based on actual usage. This applies to assets and other applications, including industrial processes, which may be evaluated using actual data to respond to evolving needs, specifications, or market circumstances.
A digital twin is distinct and real-world, whereas a simulation is conceptual.
For example, consider the application of digital twins in healthcare. Data from many medical equipment and sensors can generate a Digital Twin of a patient's health in a hospital setting. This twin offers a current representation of the patient's state. It assists medical professionals in making accurate and timely judgments based on the patient's health status rather than on guesses or data from the past.
Conversely, retailers plan their store layouts using simulations. By strategically placing walkways and displays and modeling customer movement and behavior, they can boost revenue and improve the shopping experience.
4. Use Cases and Applications
With digital twins' ever-changing, real-time perspective of actual resources and processes, many applications that improve operational effectiveness and decision-making are made possible.
Predictive maintenance is one of the most vital uses of digital twins. Digital twins can anticipate when maintenance is required. This eliminates unplanned breakdowns and decreases downtime. They do this by constantly tracking the functioning and efficiency of machinery.
Digital twins give continuous evaluation and administration by providing tangible items, a current, live digital equivalent.
Take the example of digital twins in the construction industry. Building managers use digital twins to track security, lighting, and HVAC systems in real-time. This guarantees peak performance, low energy consumption, and prompt problem-solving.
Even though they are not real-time, simulations are invaluable tools for examining various outcomes and situations based on predetermined information and hypotheses. Before designs are implemented, they must be tested, trained, and validated.
Without the necessity for trials in the actual world, simulations enable the investigation of different scenarios and results. Additionally, simulations offer a secure and regulated setting for staff training in intricate and dangerous tasks.
For instance, automakers test the safety of the following model years using accident simulations. By simulating various collision scenarios, they can find and fix potential safety issues without expensive physical crash tests.
Also Read: 10 Examples of Digital Twin Technologies for Industries. Here

/f/122804/1600x602/bcdf1cebd5/digital-twin-vs-simulation.jpg)



/f/122804/1999x753/439aec19e6/digital-twins-in-construction.webp)
/f/122804/1999x787/a929d7e402/digital-twins-in-supply-chain.webp)
/f/122804/2048x771/ac92debea8/leading-digital-twin-service-providers-for-smart-cities-in-2025.webp)