Implementing Digital twins in healthcare comes with several challenges. Here are a few pointers for you to consider.
Data security and privacy

It requires a massive amount of personal health data for the use of digital twins in healthcare. The data isn't just sensitive but also the most private information individuals have. It is crucial to protect these data's security and privacy as a result.
An instance of a data privacy breach may be insurance fraud or identity theft. In extreme circumstances, a patient might even become the subject of discrimination because of their health. For example, in cases where the patient's prognosis is poor, the insurance company may decide not to cover the new medication.
For these reasons, before deploying digital twins, healthcare organizations should make sure that improved data privacy and security procedures are in place. The first step is to encrypt all data, both in transit and at rest. Ensure that the data is only accessible to those who are allowed. In order to monitor who is accessing the data and when, keep up with the audit logs.
Best practice? Comply with regulations like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
These regulations put stringent requirements for the handling of personal data.
Data accuracy and completeness
To effectively portray a patient's health, digital twins need access to a complete set of medical data. For the digital twins to be effective, the data's completeness and correctness are therefore essential.
The following are some of the elements that affect how accurate and complete data is.
Medical history - It's imperative to get a thorough medical history from the patient.
Genetic information - Genetics can be a key reason for certain diseases. Therefore it's crucial to get it, but in reality, it may not be feasible or ethical to do so.
Lifestyle factors - This includes data on the patient's diet, exercises, stress levels, and substance use.
Real-time health data - It's now possible to get real-time health data with wearable technologies. But the data from it can't be 100% accurate as the patient could not have always worn the device.
As a result, collecting and integrating such a wide array of data is a significant challenge.
Interoperability
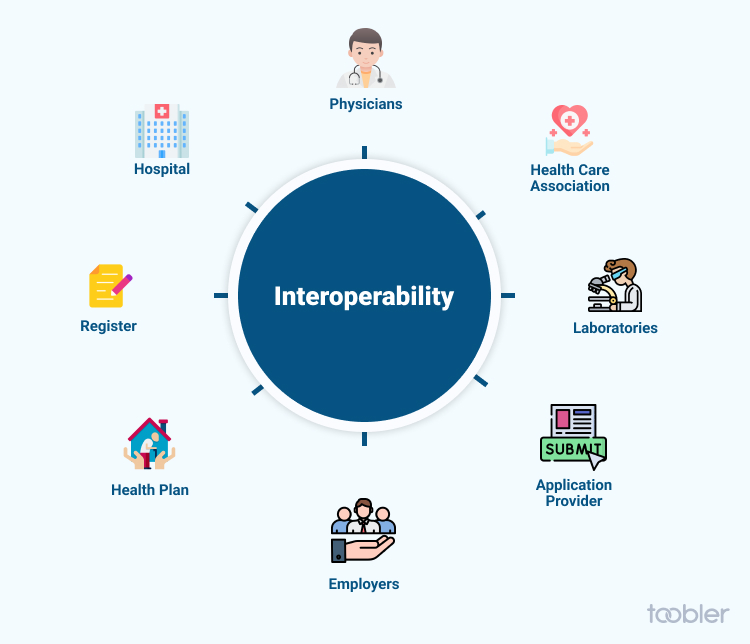
Another major challenge when it comes to implementing digital twins is interoperability. Healthcare is scattered across various systems, each having different data standards, formats, or terminologies. This makes it difficult to share and combine data accurately.
To give you an example, the patient's electronic health record might be maintained in one system, whereas the pharmacy might use a different system to manage the medication data. The labs where they test the blood might use another system. It can be challenging to get accurate data if these systems are unable to communicate and share these data.
One way to overcome this challenge is to implement proper data standardization and harmonization processes.
Technical complexity
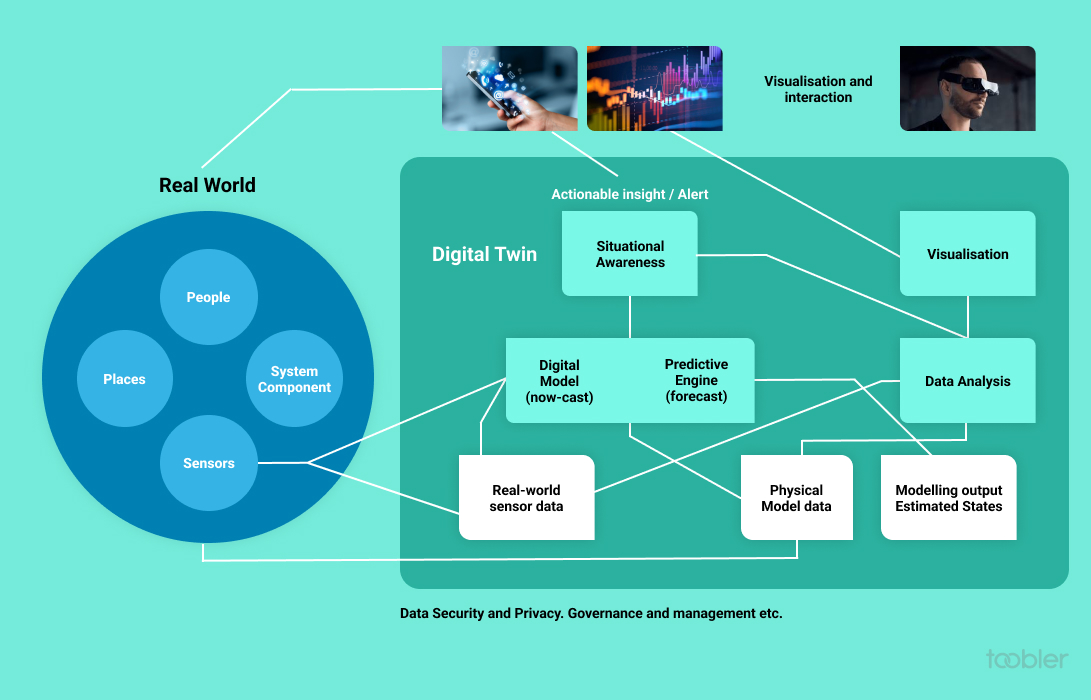
A digital twin is a cutting-edge technology that is part of the fourth industrial revolution. The level of tech expertise that is needed to create, implement and manage it is relatively high. Also, digital twins require constant updating and refinement based on real-world data.
Other factors that add up to the complexity include -
It requires sophisticated modeling and simulation techniques to create it.
It requires advanced data analytics to analyze and interpret the huge amount of data it produces.
It must be capable of integrating with existing healthcare IT systems.
As you can see from the mentioned points, it requires a healthcare provider to be technically advanced to implement digital twins. This means only larger hospitals or technologically advanced healthcare providers can install them.
Cost
The financial investment required for implementing a digital twin in healthcare is significant. Several factors influence the implementation cost, and the following are some of them.
The cost of the technology itself is high. You need several hardware, software, and networking infrastructure, all of which are costly.
The data required for digital twins must be accurate. And it is costly to collect, clean, and integrate these data into it.
If you implement it, you need personnel to manage it. This means you need to hire and train new blood, and there is only a handful who knows the tech.
Digital Twin requires constant maintenance and updates to remain effective and secure. And this could add up the cost.
As discussed earlier, it requires top-notch security measures. But implementing and maintaining these measures can be costly.
Last but not least is consultation with tech experts. You may need to hire or consult digital twin experts to guide you with the implementation process. Again, adding to the already high cost.
Though the cost is expensive, there are ways you can reduce or lower it. One way is for you to partner with a digital twin expert and outsource your tech-related work. Although it doesn't cut the cost by half, it does lower the overall cost.
Patient consent and engagement
Obtaining consent from the patient can be a challenging task, mostly because patients won't have a clue what they are consenting for. The concept of Digital twins is so complex that the patient may not always understand what it means or how it helps.
Now, even if they understand what it does, they might point out the privacy concerns they have. And not to mention the long-term implication of digital twins. The patient data needs to be collected regularly and updated into the digital twin to showcase the patient's current health status.
What can you do? Educate them.
Make the patients understand the benefits of digital twin. Be clear about the ability of digital twins to provide better and more targeted treatments for them.
And if nothing works, try to use real-world examples where digital twins have been used to treat patients.
Scaling
Expanding the implementation of digital twins from a small environment to a broader and more diverse set of conditions can be challenging. The set conditions can be anything from patient demography to different types of health conditions.
For example, initially, implementing digital twins on a small scale can be feasible, like for 100 patients. But when considering a large scale like 10,000, the complexity of data that needs to be managed is significant.
Some other challenges that you can face while scaling the digital twin are as follows.
Scaling would mean more investment and therefore become more costly.
You'll need proper IT and tech support to implement and manage the large-scale digital twins.
The need to comply with myriad regulations arises, and it is challenging to do so.
To effectively implement digital twins across different healthcare facilities, you will need to standardize certain aspects.
To overcome these challenges, building a robust collaboration between healthcare professionals, tech providers, regulators, and patients is essential.
As the tech evolves, it is possible to permanently overcome some of these challenges. And the cost will also take a hit when the competition between the service providers peak.
Also read: What is the future of digital twins?

/f/122804/1800x900/782e730704/cover-image.jpg)









 Our world is still recovering from the recent epidemic. But what if I told you Digital twins could have helped control the spread of Covid-19?
Our world is still recovering from the recent epidemic. But what if I told you Digital twins could have helped control the spread of Covid-19? 





/f/122804/2048x771/ba8f3fa521/personalized-patient-care-with-digital-twin-technology-in-healthcare.jpg)
/f/122804/2048x1147/92db62eed6/digital-twin-ai-for-enhanced-performance.webp)
/f/122804/5601x2109/e13f2e449e/application-modernization.webp)